How Is Plate Tectonics Related to Continental Drift? A Brief Overview
Plate tectonics and continental drift are two fundamental concepts in the field of geology that have revolutionized our understanding of Earth’s dynamic processes. These interconnected theories have shaped our knowledge of the planet’s structure, history, and the forces that have shaped its surface over millions of years. In this article, we will provide a concise overview of how plate tectonics and continental drift are related and how they have contributed to our understanding of Earth’s geological evolution.
Continental Drift: A Pioneering Hypothesis
To understand the connection between plate tectonics and continental drift, we must first explore the concept of continental drift.
Alfred Wegener’s Theory 🌍
In the early 20th century, German meteorologist and geophysicist Alfred Wegener proposed the theory of continental drift. He suggested that the continents were once part of a supercontinent called Pangaea and have since drifted apart over time.
Evidence of Pangaea 🌐
Wegener supported his hypothesis with geological evidence, such as the fit of the continents’ coastlines, similarities in rock formations, and the distribution of fossils across continents.
Plate Tectonics: The Mechanism Behind Drift
Now, let’s delve into the concept of plate tectonics and how it provides the mechanism behind continental drift.
Earth’s Lithosphere 🌏
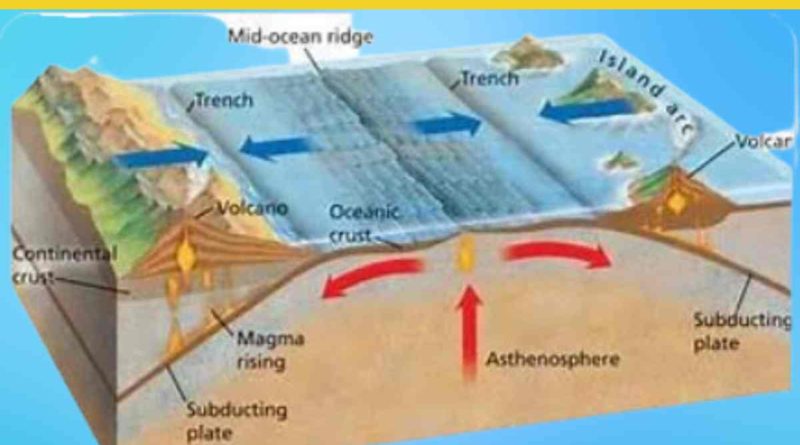
The Earth’s outermost layer, called the lithosphere, is divided into several large and small tectonic plates.
Plate Boundaries 🌋
These plates float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere beneath them and interact at their boundaries, which can be classified as divergent, convergent, or transform.
Plate Movements 🔄
The driving force behind continental drift lies in the movement of these tectonic plates. They can move apart, collide, or slide past each other, leading to various geological phenomena.
Seafloor Spreading 🌊
At divergent boundaries, such as mid-ocean ridges, new crust forms as magma rises from the mantle and solidifies, pushing the plates apart. This process is known as seafloor spreading.
Subduction Zones ⛏️
Conversely, at convergent boundaries, one plate is forced beneath another in a process called subduction. This subduction leads to the recycling of old crust into the mantle.
Follow Us On NewUsaNews Facebook Page
The Connection: Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift
The connection between plate tectonics and continental drift lies in the movement of tectonic plates.
Tectonic Plate Movement 🌌
The movement of these plates causes continents to drift, leading to the changing positions of landmasses over geological time scales.
Revisiting Wegener’s Hypothesis 🔄
Plate tectonics provided the mechanism that Wegener’s theory of continental drift lacked. It explained how and why the continents moved and addressed the forces driving these movements.
Supporting Evidence 🗺️
Plate tectonics has since accumulated substantial evidence to substantiate the theory of continental drift, including detailed mapping of plate boundaries, seismic activity, and the study of the Earth’s magnetic field patterns recorded in rocks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, plate tectonics and continental drift are intimately related concepts in geology. While Alfred Wegener’s theory of continental drift laid the groundwork for our understanding of landmass movements, plate tectonics provided the mechanism and evidence to support the idea of continents drifting over time.
The study of plate tectonics and continental drift has significantly advanced our understanding of Earth’s dynamic geological processes. It has shaped our comprehension of mountain-building, earthquakes, volcanic activity, and the distribution of natural resources.
As scientists continue to explore the complexities of plate tectonics and unravel the mysteries of our planet’s geological history, we gain further insight into the forces that have shaped and continue to shape the world we live in.